Overview of Steam Turbines: Operation, Types, Components, and Maintenance
Steam turbines are machines that convert thermal energy from pressurized steam into mechanical energy, which is then used to generate electricity or perform mechanical work in various industrial applications. They are commonly used in power plants, refineries, chemical plants, and other industries that require large-scale power generation or mechanical drive systems. Here's an overview of steam turbines:
A Guide Of Components And How Does Steam Turbine Work?
- Basic operation: Steam turbines operate on the principle of the Rankine cycle. High-pressure steam is supplied to the turbine, where it enters a series of rotating blades or buckets. As the steam flows over the blades, it imparts a force that causes the rotor to rotate. The rotation of the rotor generates mechanical energy, which can be harnessed for power generation or other applications.
- Types of steam turbines:
- Impulse turbines: In impulse turbines, the steam expands and changes direction as it passes through a set of fixed nozzles called "nozzles" or "diaphragms." The high-velocity steam jets strike the blades, known as "buckets," and cause the rotor to rotate. Impulse turbines are commonly used for low-pressure and small-capacity applications.
- Reaction turbines: Reaction turbines are characterized by the partial reaction of steam pressure as it passes through both fixed and moving blades. The steam expands continuously as it flows over the fixed and moving blades, resulting in increased velocity and pressure drop. Reaction turbines are typically used for high-pressure and large-capacity applications.
How Does Gas Turbine Works In Combined Cycle Plants
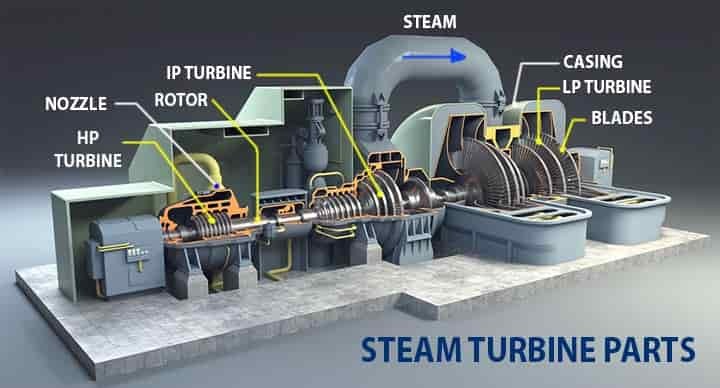
3. Components of a steam turbine:
- Rotor: The rotor is the central rotating component of the turbine. It consists of a shaft and a series of blades or buckets mounted on it. The rotation of the rotor generates mechanical energy.
- Nozzles or diaphragms: Nozzles or diaphragms are fixed guide vanes that direct the flow of steam onto the rotor blades. In impulse turbines, they control the steam flow and its velocity.
- Blades or buckets: Blades or buckets are mounted on the rotor and are designed to extract energy from the steam as it passes over them. They come in different shapes and sizes based on the specific design and application requirements.
- Casings: Casings enclose the rotor and blades and provide structural support. They also help control the flow of steam through the turbine.
4. Steam supply and exhaust: Steam is supplied to the turbine from a boiler or steam generator at high pressure and temperature. After passing through the turbine, the steam is exhausted and condensed back into water for recirculation in a closed-loop system. The condensed water is then returned to the boiler for re-heating and conversion back into steam.
Troubleshooting Common Issues & Solutions for Steam Turbines
5. Maintenance and operation: Proper maintenance and operation are essential for the efficient and reliable performance of steam turbines. Regular inspections, lubrication, and monitoring of parameters such as temperature, pressure, and vibration are necessary. Periodic maintenance tasks, including blade cleaning, seal replacement, and bearing inspections, should be performed as recommended by the manufacturer.
6. Efficiency and performance: Steam turbines can achieve high levels of efficiency, especially in combined cycle power plants, where waste heat from the turbine exhaust is utilized in a secondary system. Efficiency can be improved through advanced designs, optimized operating conditions, and upgrades to components such as blades, seals, and control systems.
For More Information Follow Mechanical Knowledge Factory
Steam turbines are complex machines, and their design and operation can vary depending on the specific application and industry. It is important to consult manufacturer documentation, industry standards, and experienced professionals when working with steam turbines to ensure safe and reliable operation.